When discussing digital transformation in the context of implementing eCommerce for B2B, the extent to which an organization has adopted and integrated digital technologies into its operations, culture, and business strategies will play a critical role in determining the success of such efforts.
Before embarking on any significant digital transformation journey, it is crucial for companies to first assess their current level of readiness to adapt to technological change, optimize processes, and provide exceptional customer experiences—all of which are key to thriving in the competitive B2B eCommerce landscape. In this article, we will look at the different stages that can be identified when assessing the degree of Digital Maturity in an organization, specifically applied to B2B eCommerce.
TMO has 10+ years of experience helping brands optimize their digital assets and developing Custom B2B eCommerce Solutions for projects in China and overseas.
Understanding Digital Maturity: Key Aspects to Evaluate
A recent survey conducted by TMO Group among eCommerce professionals underscores the importance of digital transformation for long-term success in the B2B eCommerce landscape. Respondents highlighted digital transformation as a key component of their strategies, but they also pointed out significant challenges, such as adapting legacy systems and managing complex data integrations:
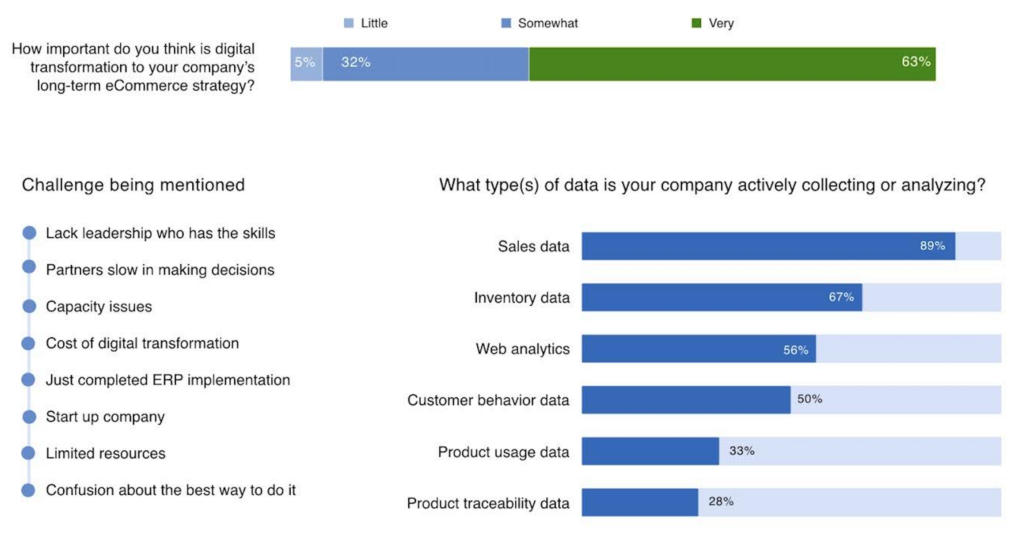
In other words, a digitally mature organization is not merely one that uses advanced technology but one that strategically incorporates digital thinking and practices throughout all aspects of its business. It involves seamless integration of systems (e.g., eCommerce, ERP, CRM), data-driven decision-making, and fostering a digital-first culture with skilled talent to lead and sustain change. Digital maturity progresses through stages, starting from basic adoption of digital capabilities to achieving advanced, automated, and data-optimized operations.
When looking at these challenges, we can effectively assess digital maturity by focusing on four critical pillars within each stage:
- 1. User Experience (UX): Foundational to digital maturity, it encompasses all aspects of the customer's interaction with the company's digital platform—from browsing products to completing purchases. As businesses mature, UX becomes more data-driven and tailored, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
- 2. System Delivery and Operation: Efficient system integration is vital for streamlining business processes and enhancing operational efficiency. At lower levels of maturity, systems may operate in silos, leading to inefficiencies and manual interventions. Mature companies use integrated systems and automation to reduce errors, increase data accuracy, and improve response times.
- 3. Data Analysis Management: Data management and analysis allow businesses to make informed decisions and drive strategic initiatives. While entry-level businesses focus on descriptive analytics (answering "what happened?"), mature companies transition to diagnostic, predictive, and even prescriptive analytics, unlocking insights that drive business growth and innovation.
- 4. Digital Talents: A digitally mature organization requires a workforce skilled in both technology and data-driven thinking. As digital maturity progresses, companies cultivate cross-functional teams with IT expertise, data literacy, and a strategic mindset, enabling them to lead innovation and maximize digital opportunities.
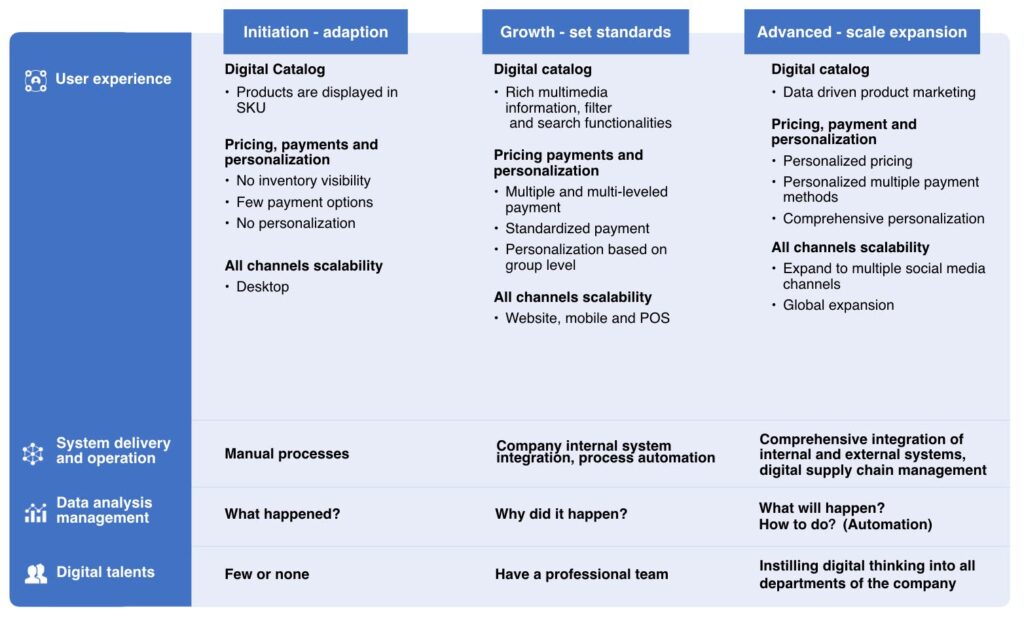
Having understood this, let's take a look at how businesses operate in each stage of digital maturity:
1. Initial Phase – Adaptation
At this stage, companies attempt to adopt digital methods to communicate with users, streamline internal processes, and begin digital analysis in order to adapt to new trends. However, the overall state remains basic: customers cannot pay online, and operations rely heavily on manual intervention.
User Experience
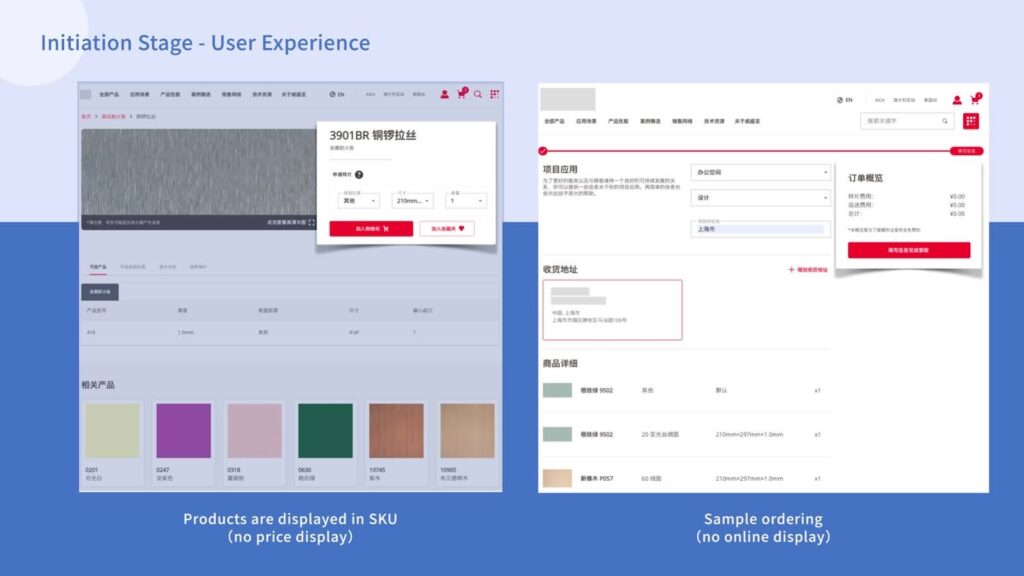
- Digital Catalog: Products are displayed as SKU, including product ID and basic specifications, and a simple product picture, if any. There is no price or inventory visibility.
- Pricing, Payment, and Personalization: Since the pricing range is not shown and there's no option to purchase online, orders take place through a contact form, telephone, or email inquiry. There is no personalization or expedited sample ordering.
- Scalability: Single channel (most of the time a desktop website, but sometimes a mobile app) with little or no social media presence.
System Establishment, Delivery, and Operation
- Sales and Fulfillment: Manual data entry into spreadsheets as well as for order processing, freight billing, and scheduling.
- Systems: Standalone applications, which means that data cannot be synchronized between eCommerce, ERP, CRM, and warehousing, leading to high labor costs and room for errors.
- Operator feedback is key here for future system implementations.
Data Management and Analysis
- Data Collection: Primarily centered around website traffic, page statistics, and basic user browsing behavior.
- Analysis: Focuses on determining "what happened" by reviewing dashboards and reports to extract insights.
- Business decisions are still based on assumptions about partially unanalyzed data.
Digital Talent
- Unlikely to have extensive IT or digital capabilities.
- The majority of employees may have more experience with traditional offline work.
- Focus on marketing and business development rather than digital initiatives.
2. Intermediate Phase – Establishing Standards
At this stage, businesses have completed the initial steps of digitalizing their operations and are starting to focus on enhancing the user experience. Companies are also beginning to automate internal system integration and processes, marking the transition to a phase where standards are established.
User Experience
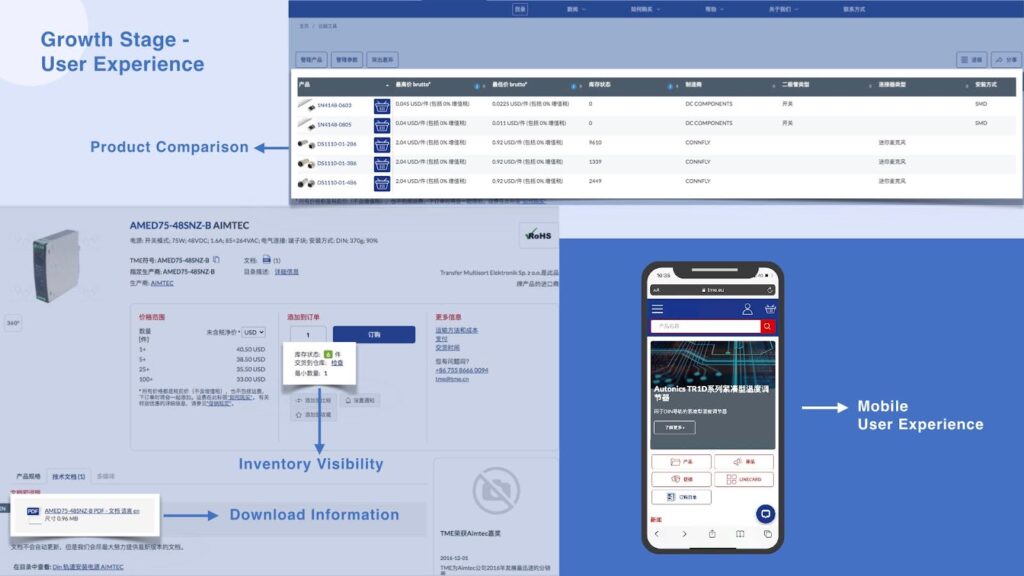
- Digital Catalog: There is additional product information beyond SKU, as well as more search, filtering, and comparison options for products. Multimedia information—pictures, videos, or PDF downloads, recommendations based on product relevance to increase order value, and online customer service are additional features.
- Pricing, Payment, and Personalization: We start to see tiered or customer group pricing, as well as standardized payment methods, online payment for fixed pricing, offline cash-on-delivery, or company credit options. There is a standardized sales process and customer account dashboards including order tracking, loyalty systems, and other personalized information.
- Scalability: Expands from desktop only to mobile and offline POS terminal, bringing a consistent user journey across channels and omnichannel delivery or process tracking.
System Establishment, Delivery, and Operation
- Sales and Fulfillment: Some manual tasks like order fulfillment, financial, and inventory management are automated, with organizational workflows being gradually optimized.
- Systems: ERP is the primary source that integrates with platforms like CRM and WMS systems.
- Real-time inventory visibility, warehousing, and third-party logistics are enabled.
- Enterprise e-invoicing, and returns/exchanges are now available.
Data Management and Analysis
- Data Collection: Multiple touchpoints including products, user behavior, and operational processes turn customer data into actionable insights
- Analysis: Transition from "what happened" to "why did it happen" involves identifying patterns in data and sentiment analysis.
- As a company becomes more digitally mature, diagnostic tasks can also be solved through data mining and machine learning techniques.
Digital Talent
- Requires personnel and software capable of generating insights, as well as a digital mindset.
- All departments of the company will need to appoint personnel who can coordinate digital transformation.
3. Maturity Phase – Scaling and Expansion
At this stage, the company's digitalization is mature, providing users with an increasingly excellent experience. The company's internal and external systems are fully integrated with digital management. Business development will focus on expanding digitalization and adopting new operational models.
Read how Magento: Key Features for B2B eCommerce GrowthAdobe Commerce (Magento) is a powerful eCommerce Solution, check out our overview of the top B2B features for enterprises.Adobe Commerce (Magento) is packed with powerful features for B2B eCommerce to fuel your brand's growth.
User Experience
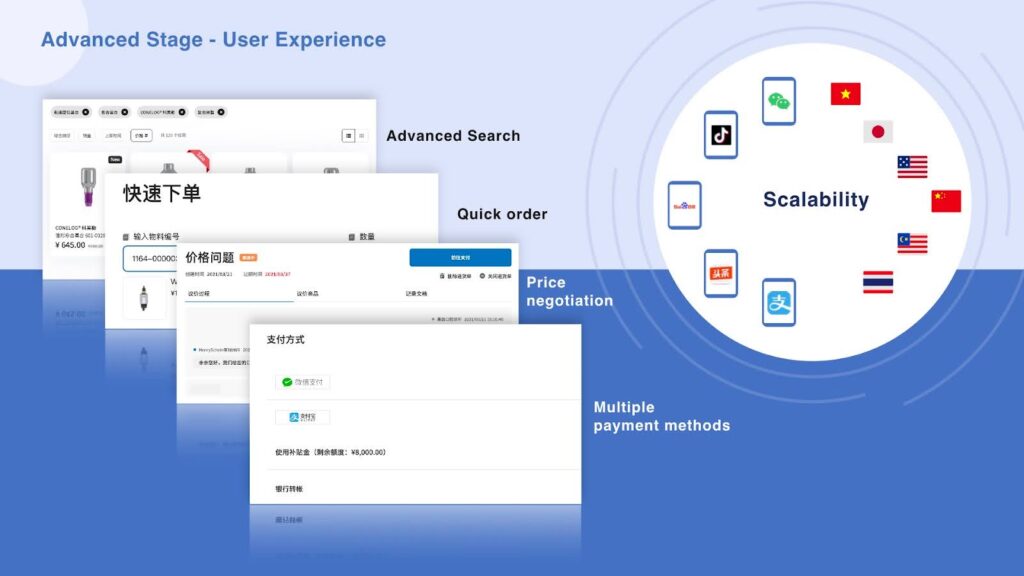
- Digital Catalog: Advanced search options, such as by product specifications, make the purchasing process more accurate and efficient for users. There are more dynamic product recommendations based on AI, as well as support for multi-market, multi-currency, multi-language, and localized catalogs that can be managed using a Product Information Management (PIM) system.
- Pricing, Payment, and Personalization: Supports multidimensional pricing strategies, such as customized, exclusive offers, and online bargaining. Payment methods based on customer type such as online (WeChat, AliPay, transfers) and offline (transfers, purchase orders, credit) are also now possible along ordering modes like subscription and automatic replenishment.
- Scalability: Expansion to social media channels, a digital store with complete inventory, and global market expansion.
System Establishment, Delivery, and Operation
- API orchestration allows for greater integration with external supply chain partners, automating workflows and reducing manual input for higher accuracy and efficiency.
- AI and big data are used for scheduling and optimizing freight management and delivery, which allows for the optimization of freight rates, as well as integrating company data and processes.
- The usage of a PIM system provides companies with a centralized location to collect, manage, and enrich complex product catalog information for distribution across online and offline channels. This ensures company-wide consistency in product information, complementing the more basic information acquired from SKU/SPU-based systems such as the company's ERP or Order Management System (OMS).
- The sales team follows up with customers through mobile CRM systems, and clienteling can solidify long-term relationships between the company and the customer. Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots primarily support customer service and after-sales, optimizing the sales funnel with 24/7 support and immediate answers to customer queries.
- Through quantitative supply chain optimization, the company leverages its digital resources to optimize supply chain operations. Companies can partner with distributors to offer offline services such as after-sales and installations.
- The partner ecosystem, incorporating marketing, consulting, and financing, is integrated to provide more efficient and transparent services.
- All company departments use a single sign-on (SSO), improving data security and lowering IT costs.
Data Management and Analysis
- Collection: Data integrated through AI and big data-driven analysis becomes increasingly important.
- Analysis: Predictive analysis focuses on "what will happen", for example, to predict whether a user will churn, how a product should be priced, or how long it will take for a machine to be serviced under current workload conditions, while Normative analysis ("what should be done") can provide recommendations such as whether to decline or prepay orders for certain customers.
Digital Talent
- Digital is at the core of the company’s work culture
- eCommerce is now fundamentally decentralized, with every team possessing certain digital skills for autonomous assessment and for devising key strategies.
The Roadmap to B2B eCommerce Implementation
By evaluating each of the variables mentioned above, you can roughly have an idea of where your current B2B operation stands, and the level of readiness it has to face digital transformation and technology adoption. Having this in mind, eCommerce implementation can be broken down into 4 steps:
For more detailed guidance on the key phases with actionable steps, read our B2B eCommerce: 4 Phases for your Digital Transformation JourneyWe explore some of the ways B2B eCommerce digital transformation can help your brand, and the steps you can take to succeed.B2B eCommerce in Phases: Starting Your Digital Transformation Journey
- Step 1: Digital Product Catalog - As the first step in B2B e-commerce, building a comprehensive digital product catalog is key. Focus on product navigation, filtering, and search functions to create an excellent user experience, providing users with detailed product information, rich product data, and brand insights. Inquiry features allow for a deeper understanding of user interests and needs.
- Step 2: Standardized B2C/B2B E-commerce - Sales capabilities must be established to attract new customers while maintaining current customers. Standardize and simplify the online purchasing process while automating workflows and sales operations.
- Step 3: Personalized B2B E-commerce Operations - Leverage deep localization and B2B-specific features to optimize your e-commerce operations and sales. Provide digitized workflows to reduce service turnaround time, offer flexible pricing and payment methods, and establish an account hierarchy to deliver exceptional services to B2B clients.
- Step 4: Scaling/New Business Models - Expand from a successful market to new markets, regions, and eventually international expansion. Explore and adopt new digital business models to meet the growing and changing demands of the market.
How TMO can guide you to full Digital Maturity
Achieving full digital maturity in eCommerce requires a strategic, phased approach that evolves alongside technological advancements and market demands. Organizations must continually assess their progress, adapt to new tools and trends, and foster a culture that prioritizes innovation, integration, and data-driven decision-making.
Building a solid digital foundation, optimizing processes, and leveraging advanced technologies are crucial steps—but equally important is the commitment to continuous learning and improvement. As companies refine their digital capabilities, they become more agile, responsive, and better equipped to deliver exceptional experiences that drive sustained growth and competitive advantage in the eCommerce landscape.
TMO specializes in crafting tailor-made digital experiences for B2B users, as well as developing integrated systems and procurement flows that can support your digital operation. If you'd like to know more about how your B2B brand can benefit from digital transformation or eCommerce integration, don't hesitate to contact our experts at TMO and discuss which online strategy might be the best fit for you.